Introduction: Garden Zones and Rhode Island
Garden zones are essential for gardeners as they provide valuable information about the specific climatic conditions of an area, which directly impacts the success of plant growth. When it comes to Rhode Island, determining which garden zone it belongs to is crucial for gardeners to make informed choices about the types of plants that will thrive in their gardens. In this article, we will explore the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, the factors that determine Rhode Island’s garden zone, and provide insights into the specific zone that Rhode Island falls within.
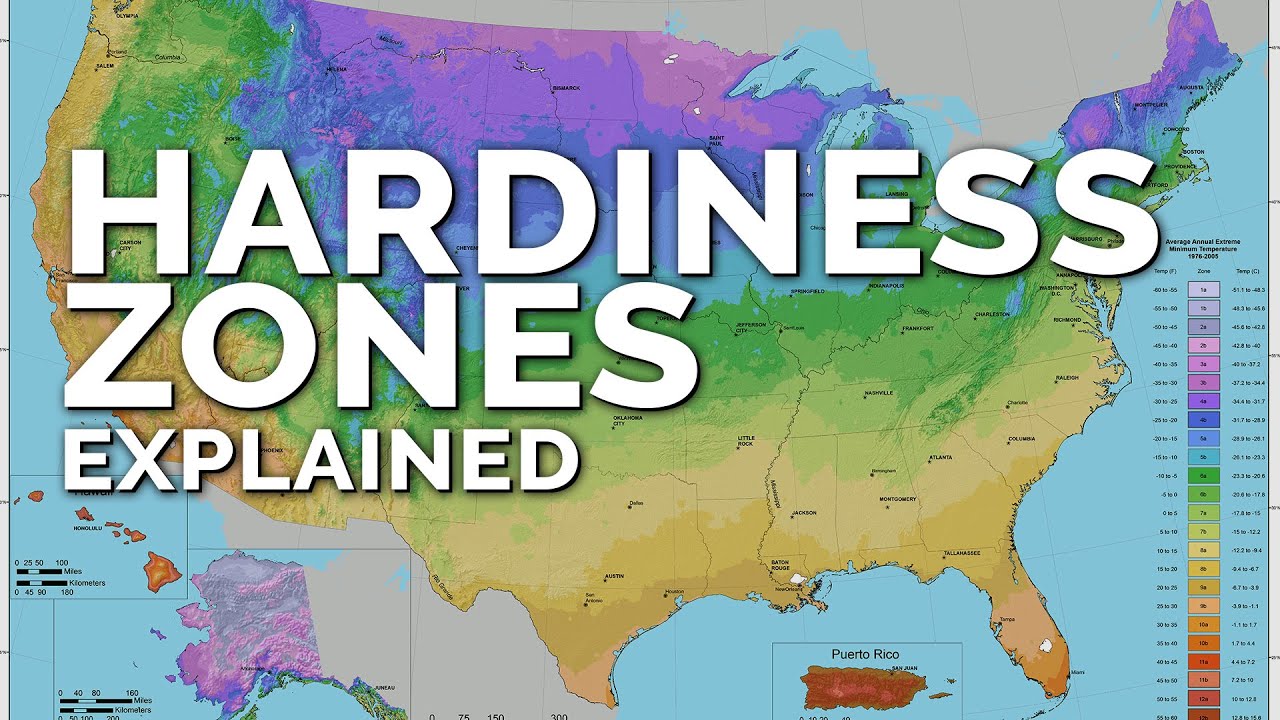
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a tool used by gardeners to determine which plants are most likely to thrive in a specific area. The map divides regions into different zones based on their average annual minimum temperatures. These zones range from 1a (colder) to 13b (warmer), with each zone having a 10°F difference in average minimum temperatures. By knowing which zone an area falls within, gardeners can select plants that can handle the local climate conditions.
Factors Determining Rhode Island’s Garden Zone
Several factors contribute to determining Rhode Island’s garden zone. The primary factor is its geographic location, which influences its climate, average temperatures, and precipitation patterns. Other factors such as soil composition, drainage, and vegetation also play a role in determining the garden zone. By examining these factors, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of Rhode Island’s garden zone.
Rhode Island’s Geographic Location and Climate
Rhode Island is located in the New England region of the United States, bordered by Connecticut and Massachusetts. Its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean significantly influences its climate, making it a part of the humid continental climate zone. This means that Rhode Island experiences four distinct seasons, with hot summers and cold winters.
Examining Rhode Island’s Average Temperatures
Rhode Island’s average temperatures vary throughout the year, with warm summers and cold winters. The average high temperature in the summer ranges from 80°F to 85°F, while winter temperatures can drop to an average low of 20°F to 25°F. These temperature ranges are crucial in determining the specific garden zone within which Rhode Island falls.
Analyzing Rhode Island’s Annual Precipitation
Rhode Island receives an average annual precipitation of approximately 45 inches. This rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year, ensuring a consistent supply of water for plants. However, excessive rainfall can also pose challenges, particularly in terms of soil drainage, which we will explore further in the next section.
Rhode Island’s Soil Composition and Drainage
Rhode Island’s soil composition varies across the state, ranging from sandy soils near the coast to loamy soils further inland. The soil’s ability to drain excess water is crucial for plant growth. Some areas may have well-drained soil, while others may have poor drainage. Understanding the soil composition and drainage characteristics is vital for successful gardening in Rhode Island.
Vegetation and Plant Life in Rhode Island
Rhode Island is home to a diverse range of vegetation and plant life. The state’s forests consist of a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees such as oak, maple, pine, and cedar. Coastal areas are characterized by salt-tolerant plants like beach grass and bayberry. The variety of vegetation in Rhode Island reflects the adaptability of plants to different garden zones within the state.
Rhode Island’s Garden Zone: Zone X
Based on the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, Rhode Island falls predominantly within Zone X. This zone encompasses areas with average minimum temperatures ranging from -10°F to 0°F. Gardeners in Rhode Island should select plants that can survive and thrive under these temperature conditions to ensure successful gardening.
Plant Selection and Gardening Tips for Zone X
In Zone X, gardeners in Rhode Island can choose a wide range of plants that are well-suited to the region’s average temperatures. Some suitable plant options include perennials like daylilies, black-eyed Susans, and hostas, as well as woody plants like hydrangeas and viburnums. It is crucial to select plants that are cold-hardy and can withstand the winter temperatures in Zone X.
Adapting to Rhode Island’s Garden Zone Challenges
While gardening in Rhode Island’s garden zone comes with its challenges, such as cold winters and occasional extreme weather events, there are strategies to overcome them. Protecting plants during the winter with mulch, using frost covers, and selecting cold-hardy varieties are effective ways to adapt to the garden zone challenges in Rhode Island. Regular soil testing and improving drainage can also help address potential issues related to soil composition.
Conclusion: Thriving Gardens in Rhode Island
Rhode Island’s garden zone, Zone X, offers ample opportunities for gardeners to create thriving gardens. By understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, considering factors such as average temperatures, precipitation, soil composition, and drainage, and selecting suitable plants, gardeners can successfully navigate the specific challenges of gardening in Rhode Island. With proper planning and care, gardens in Rhode Island can flourish, adding beauty and enjoyment to the local landscape.