Introduction to Planting Zones
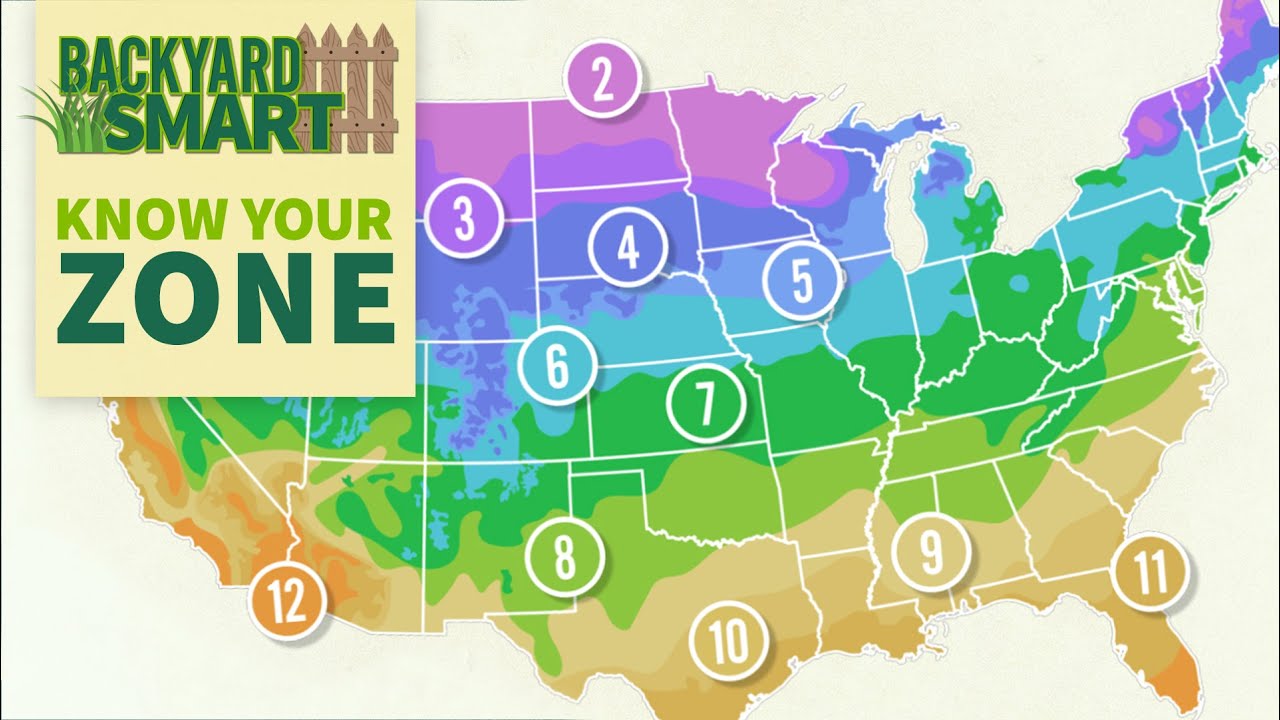
Planting zones are widely used by gardeners and horticulturists to determine the suitability of plants for a particular geographic area. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has divided the country into 11 different planting zones based on average annual minimum temperatures. These zones provide valuable information about the types of plants that thrive in each region.
Understanding the Importance of Planting Zones
Planting zones play a crucial role in successful gardening. By understanding the planting zone of a specific area, gardeners can select plants that are well-suited to the local climate conditions. This knowledge helps ensure optimal growth, flowering, and fruiting. It also aids in protecting plants from extreme weather events, such as frost or heatwaves, which can be detrimental to their health.
Defining Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States, falls within USDA hardiness zone 6a. This means that the average minimum temperature in the region ranges between -10°F (-23°C) and -5°F (-21°C). Understanding this planting zone is essential for Rhode Island gardeners, as it determines the types of plants that will thrive in the area.
Factors Determining Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
Several factors contribute to defining a specific planting zone. The primary factor is the average annual minimum temperature. However, other factors like precipitation patterns, soil composition, and microclimates within the state also influence the overall suitability of plants to thrive in a particular zone.
Climate Characteristics of Rhode Island
Rhode Island experiences a humid continental climate, characterized by hot summers and cold winters. The state’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean moderates its temperature, preventing extreme heat or cold. However, the coastal areas tend to be slightly milder than the inland regions due to the ocean’s influence.
The Role of Temperature in Planting Zones
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of plants for a region. Different plants have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth and survival. The planting zone of Rhode Island is primarily determined by its average annual minimum temperature, which affects the plants’ ability to withstand cold temperatures during the winter months.
Precipitation Patterns in Rhode Island
Rhode Island has a moderate annual precipitation of around 45 inches (114 cm). The state receives rainfall throughout the year, with the highest amounts occurring during the summer months. Adequate moisture is essential for plant growth, and understanding the precipitation patterns helps gardeners plan irrigation and select plants that are drought-tolerant or require more water.
Soil Composition in Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
Rhode Island has diverse soil types, including sandy loam, clay loam, and silt loam. The soil composition varies across the state, making it important for gardeners to understand the specific soil type in their area. Soil fertility, drainage, and pH levels significantly impact plant growth. Conducting a soil test can provide valuable information and guide gardeners in selecting plants suitable for their specific soil conditions.
Native Plants in Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
Rhode Island’s planting zone offers a wealth of native plants that are well-adapted to the local climate. Some popular native plants include the Eastern Red Cedar, Bayberry, Blueberry, Beach Plum, and Red Maple. These plants have evolved to thrive in Rhode Island’s specific conditions and provide essential habitat and food sources for local wildlife.
Planting Tips for Rhode Island Gardeners
To create a thriving garden in Rhode Island, gardeners should consider a few essential tips. First, selecting plants suitable for zone 6a is crucial. It is also important to pay attention to soil quality, providing proper drainage, and amending the soil when necessary. Additionally, gardeners should water plants adequately and consider mulching to retain moisture. Regular monitoring, pest control, and timely fertilization are additional steps that can help ensure a successful garden.
Challenges and Opportunities in Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
Rhode Island’s planting zone presents both challenges and opportunities for gardeners. The cold winters can be a challenge for certain sensitive plants, requiring protective measures such as mulching or moving containers indoors. However, the moderate summers and plentiful rainfall provide favorable conditions for a wide variety of plants, allowing gardeners to experiment with different species and create diverse and vibrant gardens.
Conclusion: Nurturing a Thriving Garden in Rhode Island
Understanding Rhode Island’s planting zone is essential for gardeners looking to cultivate a successful garden. By considering factors such as temperature, precipitation, soil composition, and native plants, gardeners can select the most suitable plants for their gardens. With proper care, attention to local conditions, and regular maintenance, gardeners in Rhode Island can nurture a thriving and beautiful garden that thrives within the unique characteristics of their planting zone.