Introduction to Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States, is located in the northeastern part of the country. It is known for its beautiful landscapes, diverse flora, and favorable gardening conditions. To understand the specific requirements for gardening in Rhode Island, it is important to determine the plant zone in which the state is located.
Understanding the Importance of Plant Zones
Plant zones, also known as hardiness zones, are geographic areas that classify regions based on their climate conditions. These zones provide valuable information to gardeners, helping them select plants that are most likely to thrive in their specific location. By understanding the plant zone of a particular area, gardeners can better plan their gardens, choose appropriate plants, and ensure their success.
Defining Rhode Island’s Climate Conditions
Rhode Island experiences a humid continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters. Its location in the northeastern part of the United States means that it is influenced by both the Atlantic Ocean and the continental air masses that move across the region. These factors contribute to the state’s unique climate conditions, which impact the plant zone in which Rhode Island is situated.
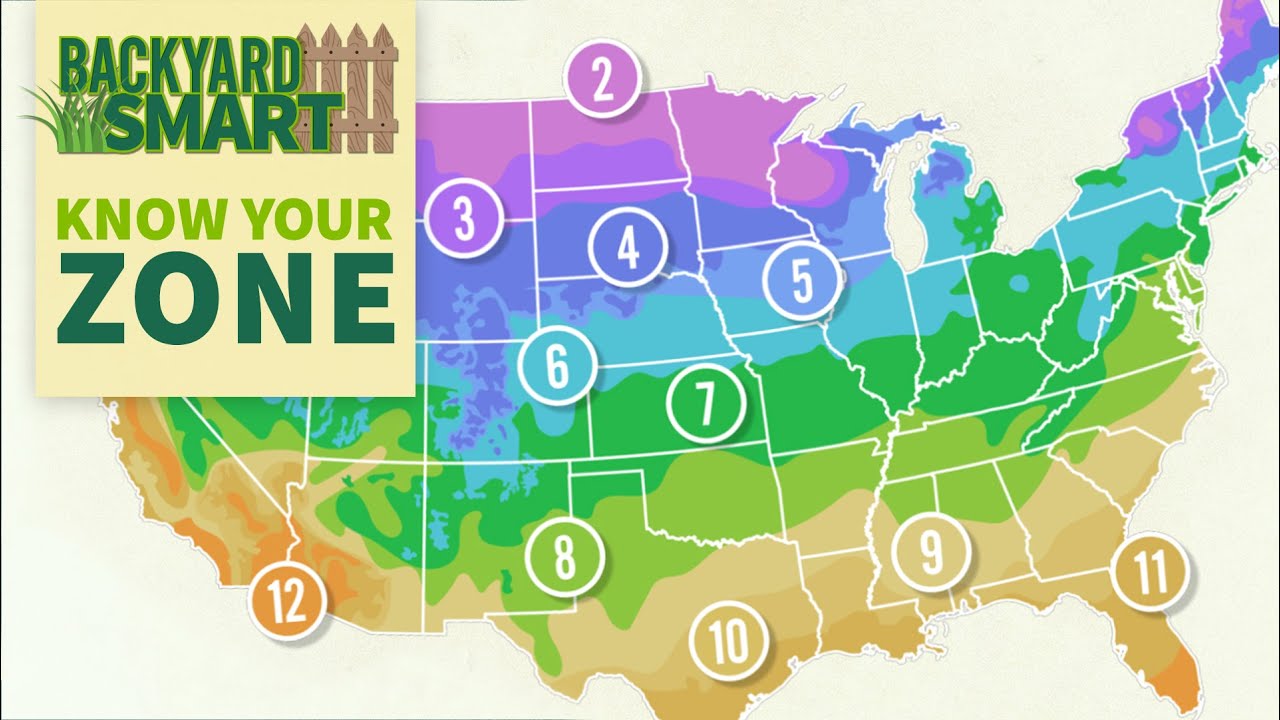
Rhode Island’s Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has developed a plant hardiness zone map that divides the country into different zones based on average annual minimum temperatures. This map provides valuable information for gardeners in determining the suitable plants for their area. Rhode Island falls within USDA hardiness zones 5b and 6a, which are characterized by average minimum temperatures ranging from -15°F (-26°C) to 0°F (-18°C).
Identifying Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
Based on the USDA hardiness zone map, Rhode Island can be identified as primarily belonging to zones 5b and 6a. This means that gardeners in Rhode Island should select plants that are hardy to these zones to ensure their survival. It is important to consider the specific requirements of each plant and their ability to tolerate the cold winter temperatures and hot summer conditions experienced in Rhode Island.
Factors Influencing Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
Several factors contribute to Rhode Island’s plant zone classification. The state’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and its maritime influence play a significant role in moderating its climate. Ocean currents help regulate temperatures, providing a milder climate compared to areas further inland. The state’s elevation and proximity to mountainous regions also influence temperature variations within Rhode Island, contributing to the determination of its specific plant zone.
Native Plants in Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
Rhode Island’s native plants are well-adapted to the local climate conditions, making them a suitable choice for gardening in the state’s plant zone. Some examples of native plants that thrive in Rhode Island include common witch-hazel, sweet fern, marsh marigold, and bluebell. These plants have evolved to withstand the region’s cold winters, hot summers, and other environmental factors that are characteristic of the plant zone.
Gardening Tips for Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
To make the most of Rhode Island’s plant zone, gardeners should carefully select plants that are suitable for the state’s specific climate conditions. It is crucial to consider the plant’s hardiness, sun and shade requirements, soil type, and water needs. Proper watering, mulching, and regular maintenance are essential to ensure the health and vitality of the garden. Additionally, understanding the local frost dates and planning accordingly can help gardeners maximize their growing season.
Challenges for Gardening in Rhode Island
While Rhode Island’s plant zone offers favorable conditions for gardening, there are some challenges that gardeners may face. The state’s coastal location exposes gardens to strong winds, which can damage plants and affect their growth. Additionally, Rhode Island’s fluctuating temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns can pose challenges to the establishment and maintenance of plants. Being aware of these challenges and taking appropriate measures can help gardeners overcome them and achieve successful gardening results.
Adapting to Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
To successfully garden in Rhode Island, it is crucial to adapt to the specific plant zone of the state. This involves selecting plants that are well-suited to the local climate conditions and taking steps to protect them from potential challenges. By being mindful of the unique characteristics of Rhode Island’s plant zone, gardeners can create thriving and sustainable gardens that enhance the natural beauty of the state.
Best Plants for Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
Rhode Island’s plant zone offers a wide range of plant options for gardeners. Some of the best plants for this zone include perennials like daylilies, asters, and coneflowers, which are known for their ability to withstand the state’s climate conditions. Additionally, shrubs such as hydrangeas, rhododendrons, and azaleas thrive in Rhode Island. Vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and lettuce also do well in this plant zone. It is important to consult with local nurseries or gardening experts to determine the most suitable plants for Rhode Island’s specific plant zone.
Conclusion: Exploring Rhode Island’s Plant Zone
Rhode Island’s plant zone, encompassing USDA hardiness zones 5b and 6a, provides valuable information for gardeners in the state. By understanding the specific requirements of this plant zone and selecting suitable plants, gardeners can create thriving and beautiful gardens. Native plants, proper gardening techniques, and adaptation to the unique challenges of Rhode Island’s climate ensure success in gardening endeavors. With careful planning and attention, gardeners can make the most of Rhode Island’s plant zone and enjoy the beauty and abundance it offers.