Introduction to Planting Zones
Planting zones are a valuable tool for gardeners, helping them determine which plants are most likely to thrive in a particular area. By understanding the planting zone of a specific location, gardeners can select plants that are well-suited to the climate and growing conditions of that region. This ensures a greater chance of successful gardening and healthy, flourishing plants.
What Determines Planting Zones?
Planting zones are determined by a combination of factors, including climate, temperature, and weather patterns. These factors influence the types of plants that can survive and thrive in a given area. While there are various methods of determining planting zones, the most widely used and recognized system is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
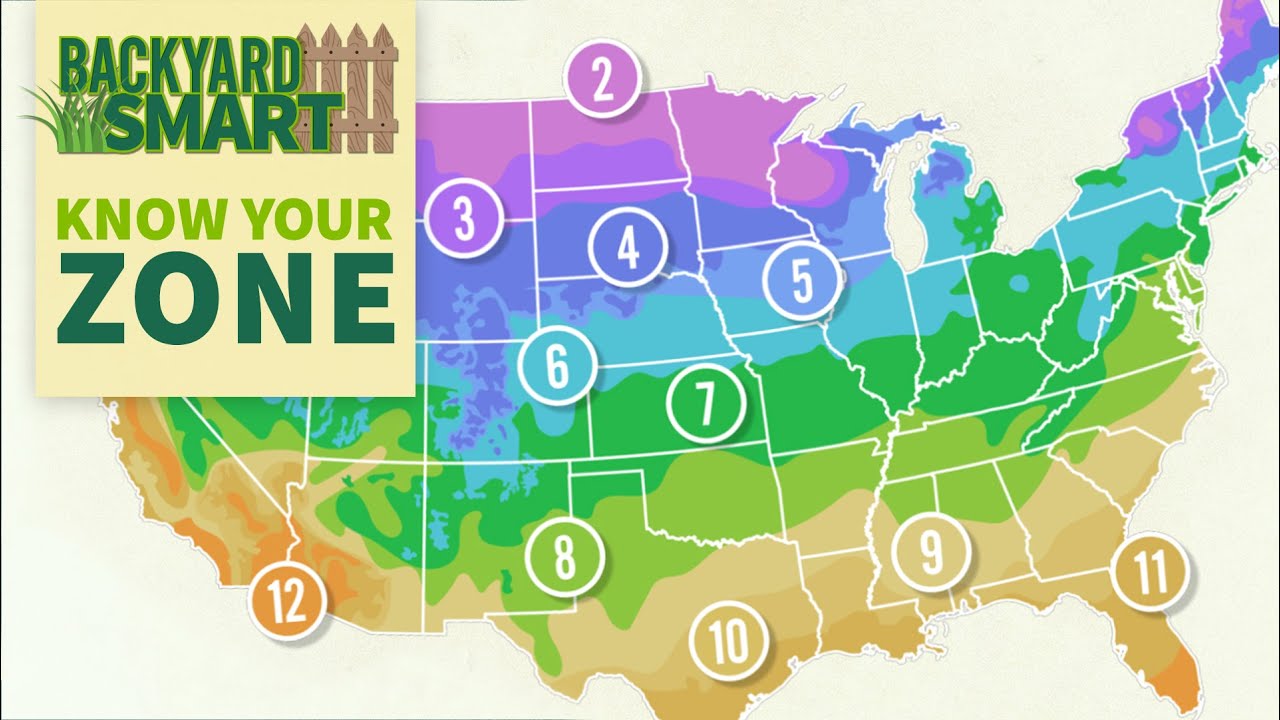
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the United States into 13 planting zones, each characterized by a certain range of minimum average annual temperatures. This map provides gardeners with a valuable resource for selecting plants that are well-adapted to their specific region. By identifying the zone in which they live, gardeners can make informed decisions about which plants to cultivate.
Rhode Island’s Geographical Location
Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States, is located in the New England region of the country. It is bordered by Connecticut to the west and Massachusetts to the north and east. With a diverse coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, Rhode Island boasts a unique geographical setting that influences its climate and weather patterns.
Rhode Island’s Climate and Weather Patterns
Rhode Island experiences a humid continental climate, characterized by cold winters and warm summers. The state also receives a significant amount of rainfall throughout the year. The proximity to the Atlantic Ocean moderates temperatures, creating mild winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas. These weather patterns play a crucial role in determining the planting zone of Rhode Island.
Rhode Island’s Planting Zone Classification
According to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, Rhode Island falls primarily under Zone 6a. This means that the average minimum temperature in the state ranges from -10°F to -5°F (-23°C to -21°C). However, small portions of Rhode Island’s coastal areas are classified as Zone 6b, where the average minimum temperature ranges from -5°F to 0°F (-21°C to -18°C).
Characteristics of Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
Rhode Island’s planting zone characteristics indicate that it is well-suited for a wide variety of plants that can tolerate moderately cold temperatures. This includes an array of trees, shrubs, perennials, and annuals. Gardeners in Rhode Island can enjoy a diverse range of plant options, allowing for a beautiful and abundant garden.
Recommended Plants for Rhode Island
For gardeners in Rhode Island, there is a plethora of plant options that are well-suited to the state’s planting zone. Some recommended plants include hydrangeas, azaleas, rhododendrons, hostas, daylilies, asters, and various types of roses. Additionally, vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, and beans can thrive in Rhode Island’s climate.
Tips for Successful Gardening in Rhode Island
To ensure successful gardening in Rhode Island, there are a few tips to keep in mind. First, it is essential to plant frost-tolerant varieties and to pay attention to the specific needs of each plant. Taking advantage of the state’s moderate summers and fertile soil can also contribute to gardening success. Additionally, proper watering, mulching, and regular maintenance are crucial for maintaining healthy plants.
Challenges of Gardening in Rhode Island
Despite its favorable planting zone, Rhode Island does present some challenges for gardeners. The state’s unpredictable weather can pose a threat to plants, with winter frost, springtime freezes, and occasional summer droughts. Furthermore, pests and diseases common to the region can impact plant health. Gardeners must be vigilant and take necessary precautions to mitigate these challenges.
Adapting to Rhode Island’s Planting Zone
With proper planning, care, and adaptation, gardeners can overcome the challenges of Rhode Island’s planting zone. By selecting hardy plant varieties, providing adequate protection during extreme weather conditions, and implementing pest management strategies, gardeners can ensure their plants’ health and promote successful gardening in the state.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Rhode Island falls under USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 6a, making it an ideal location for a wide variety of plant species. Gardeners in the state can take advantage of the moderate climate and fertile soil to create beautiful and thriving gardens. By understanding the characteristics of Rhode Island’s planting zone and implementing appropriate gardening practices, residents can enjoy the rewards of successful gardening in this charming New England state.