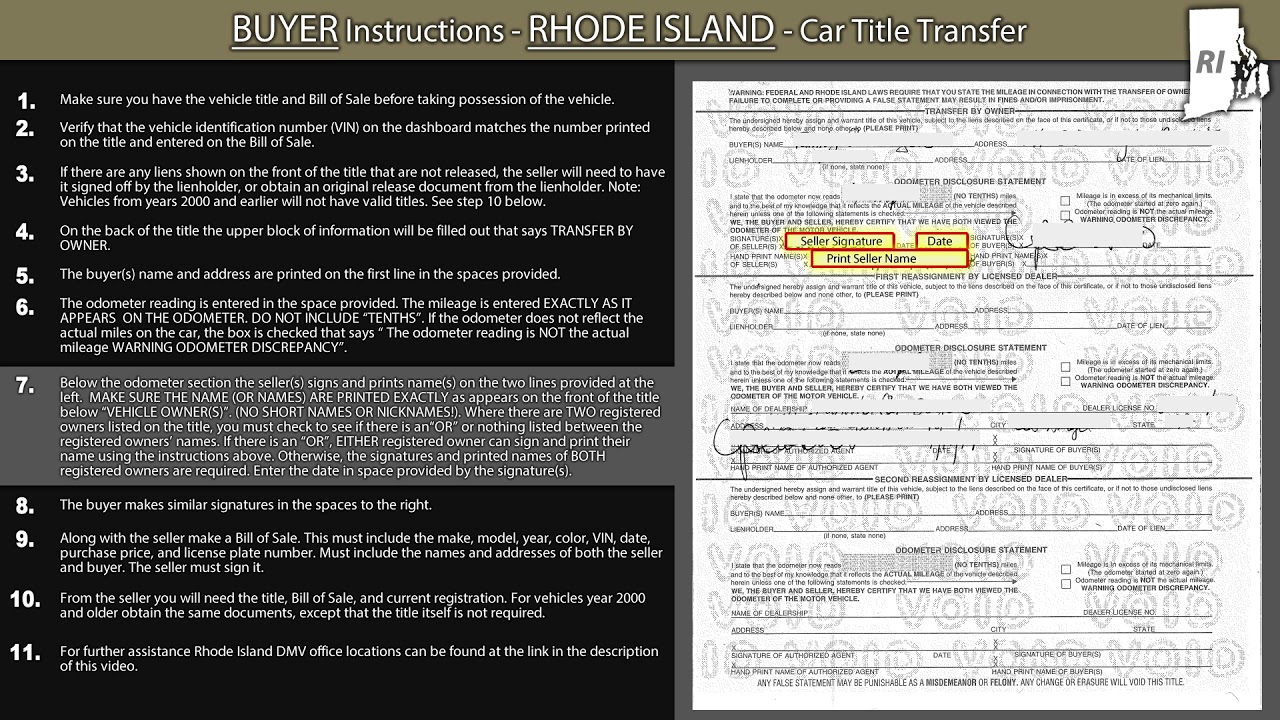
Introduction: Rhode Island’s Taxation on Pension Payments
Rhode Island, like many other states, is facing significant financial challenges. In an attempt to address these challenges, the state has implemented and considered various measures, including taxation on pension payments. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the necessity of imposing taxes on pension payments in Rhode Island. By examining the current tax laws, economic consequences, legal aspects, and comparing with other states, we can evaluate the need for such taxation.
Understanding the Current Tax Laws in Rhode Island
Currently, Rhode Island imposes taxes on pension payments. The state law subjects all retirement income, including pensions, to the state’s personal income tax. This means that individuals who receive pension payments must report them as taxable income and pay the applicable income tax rate. However, the state does provide certain exemptions and deductions for pensioners based on their income level and age.
Benefits of Imposing Taxes on Pension Payments
Imposing taxes on pension payments can have several benefits for Rhode Island. Firstly, it can generate much-needed revenue for the state’s coffers. With the state facing a substantial budget deficit and a pension crisis, additional revenue from taxing pension payments can help address these fiscal challenges. Secondly, taxing pension payments can promote fairness and equity in the tax system. By treating retirement income similarly to other forms of income, the burden of taxation is distributed more evenly among citizens.
Impact of Taxation on Rhode Island’s Revenue
The imposition of taxes on pension payments can have a significant impact on Rhode Island’s revenue. According to estimates, taxing pension income could generate millions of dollars in additional revenue annually. This additional revenue can be utilized to fund essential public services, address pension liabilities, and reduce the budget deficit. However, it is important to consider the potential economic consequences and public opinion while evaluating the overall impact on the state’s revenue.
Rhode Island’s Pension Crisis: A Brief Overview
Rhode Island’s pension crisis is a pressing issue that cannot be ignored when discussing the taxation of pension payments. The state’s pension system is severely underfunded, with a significant unfunded liability. Taxing pension payments can serve as a means to alleviate this crisis by generating revenue to fund pension obligations and ensure the long-term sustainability of the system.
Arguments against Imposing Taxes on Pension Payments
Despite the potential benefits, there are arguments against imposing taxes on pension payments in Rhode Island. Opponents argue that taxing pension payments can place an undue burden on retirees who rely on fixed income. They contend that retirees have already contributed their fair share throughout their working lives and that taxing their pensions may lead to financial hardships for many individuals.
Examining the Economic Consequences of Taxing Pensions
The economic consequences of taxing pensions are a crucial aspect to consider. Some argue that taxing pension payments could discourage individuals from retiring in Rhode Island, resulting in a brain drain and potentially harming the state’s economy. Additionally, it may impact consumer spending and reduce the overall economic activity in the state. However, proponents argue that the economic impact might be minimal, as retirees tend to have a relatively stable and predictable spending pattern.
The Legal and Constitutional Aspects of Taxing Pensions
The legality and constitutionality of taxing pensions must be taken into account. In Rhode Island, the taxation of pension payments has been upheld by the state courts. However, constitutional challenges have been raised, arguing that taxing pensions violates the contract clause and the principles of fairness. These legal aspects must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure that any taxation measures are in line with the state and federal laws.
Comparing Rhode Island’s Taxation Policy with Other States
Comparing Rhode Island’s taxation policy with other states can provide valuable insights into the necessity of taxing pension payments. Several states, including neighboring Massachusetts and Connecticut, also impose taxes on pension income. Analyzing the experience of these states can help determine the potential impact on retirees and the overall fiscal benefits of such taxation measures.
Public Opinion and Stakeholder Perspectives on Taxing Pensions
Public opinion and stakeholder perspectives play a vital role in shaping tax policies. It is essential to consider the views of retirees, labor unions, and advocacy groups who represent the interests of pensioners. While some may support taxing pensions as a means to address the state’s budget woes, others may vehemently oppose such measures. Understanding these perspectives is crucial for policymakers tasked with making informed decisions.
Potential Alternatives to Taxing Pension Payments
As an alternative to taxing pension payments, Rhode Island could consider other revenue-generating measures. These may include broadening the tax base, reducing unnecessary expenses, or implementing targeted taxes on high-income individuals or corporations. Exploring these alternatives can provide a comprehensive assessment of the feasibility and necessity of taxing pension payments.
Conclusion: Evaluating the Need for Taxation on Rhode Island’s Pension Payments
In conclusion, the necessity of imposing taxes on pension payments in Rhode Island must be carefully evaluated. While it can generate much-needed revenue, promote fairness, and address the state’s pension crisis, there are valid concerns regarding the impact on retirees and the overall economy. By considering the current tax laws, economic consequences, legal aspects, comparing with other states, and taking into account public opinion and stakeholder perspectives, policymakers can make well-informed decisions about the taxation of pension payments. Ultimately, striking a balance between fiscal responsibility and ensuring the financial well-being of retirees is crucial for Rhode Island’s future.