Introduction to Rhode Island’s Growing Zone
Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States, is located in the New England region and is known for its beautiful coastal landscapes and historic charm. When it comes to gardening and agriculture, understanding the growing zone of a particular area is crucial for successful plant cultivation. In this article, we will explore the growing zone of Rhode Island, the factors that influence it, and provide tips for gardening in this state.
Understanding the Importance of Growing Zones
Growing zones are geographical areas that are determined by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) based on the average minimum winter temperatures. These zones help gardeners identify which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific region. By understanding the growing zone of an area, gardeners can choose plants that are well-suited to the local climate and growing conditions, increasing the chances of a successful garden.
Factors Influencing Rhode Island’s Growing Zone
Several factors contribute to determining the growing zone of Rhode Island. The state’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean influences its climate, as ocean currents moderate the temperature. Additionally, the state’s small size and diverse topography, including coastal plains and hilly areas, can create microclimates that affect the growing conditions. The latitude of Rhode Island and its exposure to prevailing winds also play a role in determining the growing zone.
Rhode Island’s Climate and Growing Conditions
Rhode Island experiences a humid continental climate, with warm summers and cold winters. The proximity to the ocean helps to moderate the temperatures, resulting in cooler summers and milder winters compared to inland areas. The average annual temperature in Rhode Island ranges from around 50°F (10°C) along the coast to 45°F (7°C) in the interior. The state receives an average of 40 to 50 inches of precipitation per year, which is evenly distributed throughout the seasons.
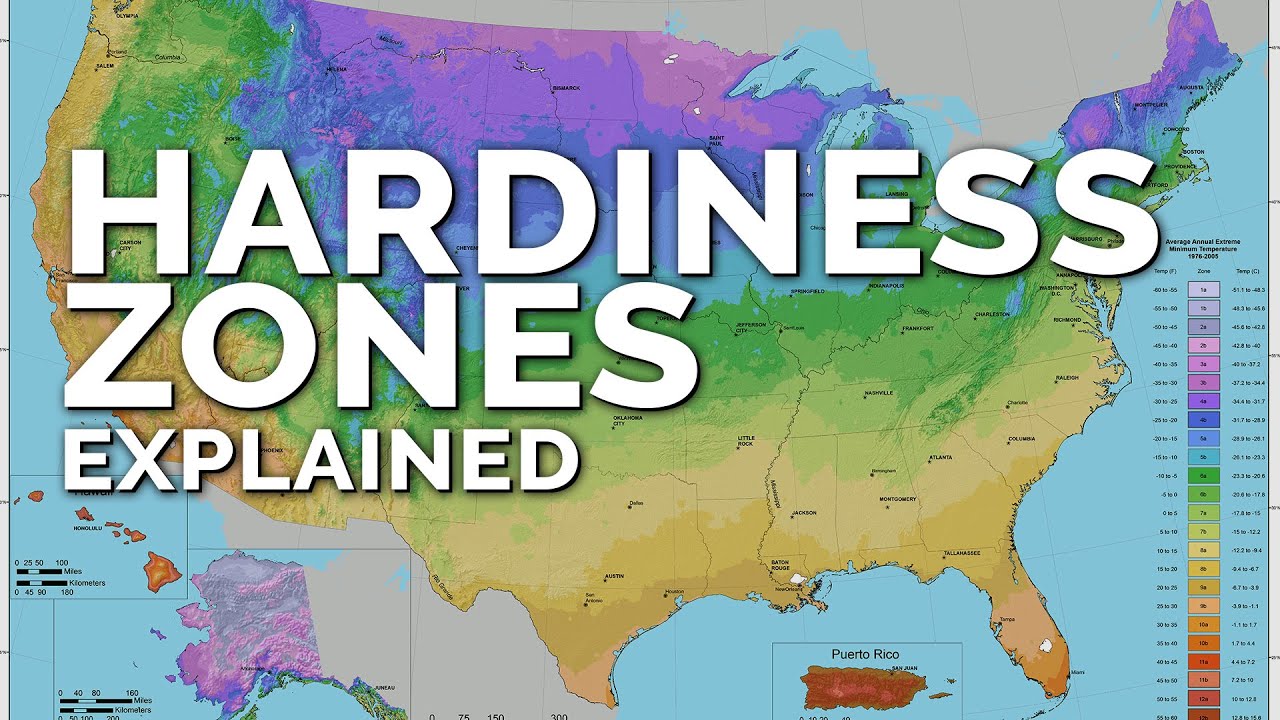
Determining Rhode Island’s USDA Hardiness Zone
Based on the average minimum winter temperatures, Rhode Island falls under USDA hardiness zones 6a and 6b. Zone 6a has minimum temperatures ranging from -10°F to -5°F (-23.3°C to -20.6°C), while zone 6b has minimum temperatures ranging from -5°F to 0°F (-20.6°C to -17.8°C). These zones are useful for selecting plants that can withstand the cold temperatures of Rhode Island’s winters.
The Role of Frost Dates in Rhode Island
Frost dates are important for gardeners as they help determine the planting and harvesting schedule. In Rhode Island, the average spring frost date ranges from late April to mid-May, while the average fall frost date occurs between late September and mid-October. These dates vary slightly depending on the specific location within the state. Understanding frost dates is crucial to avoid damage to tender plants and to maximize the growing season.
Exploring Rhode Island’s Planting and Harvesting Calendar
Rhode Island’s planting and harvesting calendar is influenced by its growing zone and frost dates. Cool-season crops, such as lettuce, spinach, and peas, can be planted as early as April, while warm-season crops like tomatoes and peppers should be planted after the last frost date in May. Fall crops, including broccoli and carrots, can be planted in late summer for a harvest before the first fall frost. Understanding the timing for planting and harvesting specific crops ensures optimal growth and yield.
Selecting Suitable Plants for Rhode Island’s Zone
Rhode Island’s growing zone is suitable for a wide range of plants. Some popular choices for this zone include perennial flowers like asters and black-eyed Susans, as well as vegetables such as potatoes, kale, and beets. It is essential to select plants that are rated for zones 6a and 6b to ensure their ability to withstand the winter cold. Local nurseries and gardening centers can provide guidance on suitable plant varieties for Rhode Island’s growing zone.
Tips for Gardening in Rhode Island’s Growing Zone
To garden successfully in Rhode Island’s growing zone, there are several tips to keep in mind. First, it is important to amend the soil with organic matter to improve its fertility and drainage. Additionally, providing adequate water and mulching to retain moisture are crucial, especially during dry periods. Regular weeding, pest control, and proper plant spacing are also essential practices for maintaining a healthy garden in Rhode Island.
Preparing Your Garden for Rhode Island’s Climate
Rhode Island’s climate requires specific preparation to ensure a thriving garden. To protect plants from harsh winter temperatures, consider applying a layer of mulch around the base of plants before the first frost. This helps insulate the soil and protect the roots. Additionally, using frost blankets or row covers can help extend the growing season in both spring and fall by providing extra insulation and protection against frost.
Adapting to Climate Change in Rhode Island
As climate change continues to impact our planet, Rhode Island, like many other regions, may experience shifts in its growing zone and climate patterns. It is important for gardeners in Rhode Island to stay informed about these changes and adapt their gardening practices accordingly. This may involve selecting more heat-tolerant or drought-resistant plant varieties, implementing water conservation measures, and utilizing techniques such as shade cloth or irrigation systems to mitigate the effects of changing climate conditions.
Conclusion: Nurturing a Thriving Garden in Rhode Island
Rhode Island’s growing zone, influenced by its climate, topography, and proximity to the ocean, offers a unique gardening experience. By understanding the growing zone and its implications, gardeners can select suitable plants, plan their planting and harvesting schedule, and implement proper gardening techniques. With careful preparation and adaptation to changing climate conditions, gardeners in Rhode Island can nurture a thriving garden and enjoy the beauty and bounty it brings.