Introduction: Understanding Hardiness Zones
Understanding hardiness zones is essential for successful gardening and landscaping. Different plants have different temperature requirements, and knowing which hardiness zone your area falls under will help you select the right plants for your garden. In this article, we will explore which hardiness zone Rhode Island falls under, along with the factors influencing the state’s zone, native plants suitable for Rhode Island’s zone, and how to protect your plants in this particular zone.
What are Hardiness Zones?
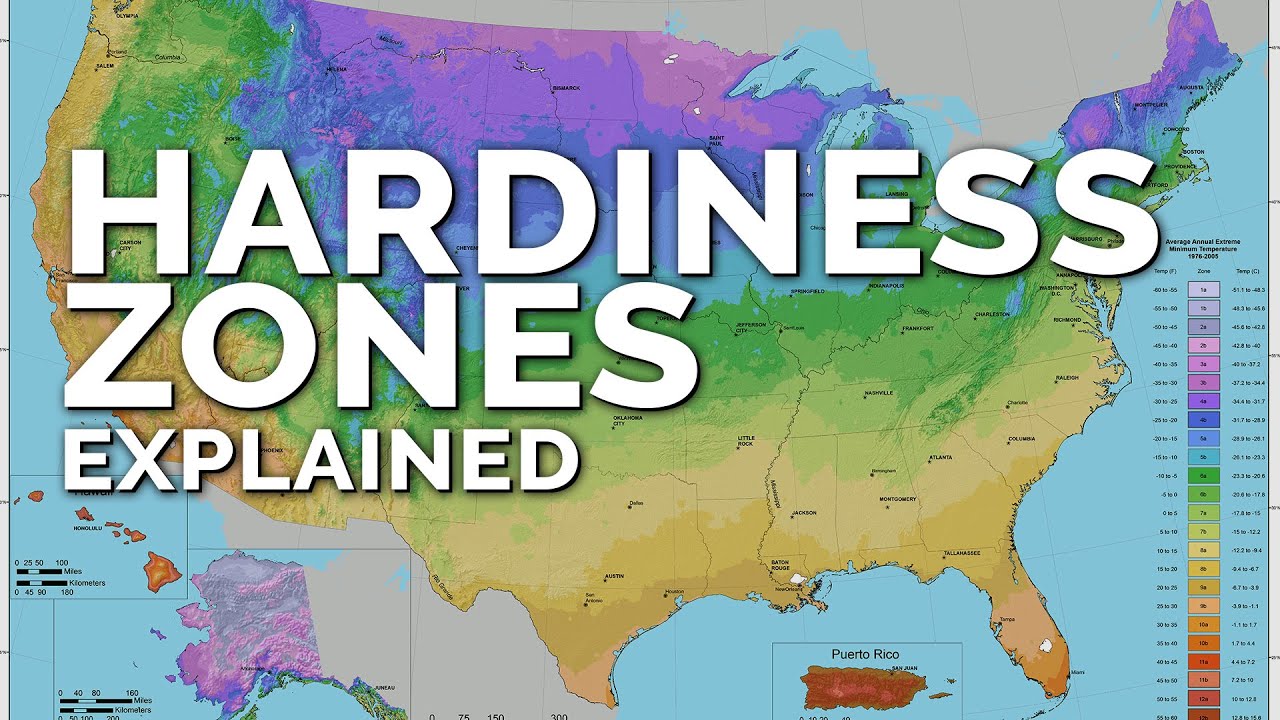
Hardiness zones are determined by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and are based on the average annual extreme minimum temperatures. The zones are divided into 10-degree Fahrenheit intervals, with each zone representing a specific range of temperatures. The purpose of the hardiness zone map is to help gardeners and farmers determine which plants are most likely to thrive in a given area based on its climate.
The Importance of Knowing Your Hardiness Zone
Knowing your hardiness zone is crucial because it provides valuable information about the types of plants that will survive and thrive in your area. When you choose plants that are suitable for your zone, you increase the chances of successful growth and reduce the risk of plants dying due to extreme temperatures. By understanding your zone, you can make informed decisions about what to plant and when to plant it.
Factors Influencing Rhode Island’s Hardiness Zone
Several factors influence Rhode Island’s hardiness zone, including its geographic location, proximity to the ocean, and its climate. These factors combine to create a unique environment that determines the zone in which the state falls.
Rhode Island’s Geographic Location and Climate
Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States, is located in the New England region of the country. It is situated in the northeastern part of the US, bordering Connecticut to the west and Massachusetts to the north and east. The state’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean greatly influences its climate, resulting in milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas.
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA hardiness zone map is widely used by gardeners and farmers across the United States. It divides the country into 13 zones, each representing a specific range of temperatures. The map is regularly updated to reflect changes in climate patterns and provides a valuable resource for understanding which plants are best suited for specific areas.
Rhode Island’s Hardiness Zone: A Closer Look
Rhode Island falls primarily into USDA hardiness zone 6b. This zone is characterized by average annual extreme minimum temperatures ranging from -5 to 0 degrees Fahrenheit. However, the southern part of the state, including coastal areas, falls into zone 7a, with temperatures ranging from 0 to 5 degrees Fahrenheit. These zones indicate that Rhode Island experiences relatively mild winters compared to many other parts of the country.
Planting Guide for Rhode Island’s Hardiness Zone
Rhode Island’s hardiness zone 6b is ideal for growing a variety of plants, including perennials, annuals, vegetables, and fruits. Gardeners in this zone can enjoy planting vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers during the warmer months. Additionally, a wide range of flowers like asters, black-eyed Susans, and daylilies thrive in this zone.
Native Plants Suitable for Rhode Island’s Zone
Native plants are well adapted to the local climate and often require less maintenance compared to non-native species. Some native plants suitable for Rhode Island’s hardiness zone include common milkweed, eastern red columbine, New England aster, and blue-eyed grass. Incorporating native plants into your garden not only supports local ecosystems but also helps conserve water and reduce the need for fertilizers and pesticides.
Adapting to Climate Change: What Does It Mean for Rhode Island?
Climate change is a pressing issue that affects gardening and landscaping practices. As temperatures and weather patterns continue to shift, it is crucial for gardeners in Rhode Island to stay informed about the changing climate and its impact on plant selection and growing practices. This may include choosing more heat and drought-tolerant plants, adjusting planting schedules, and implementing sustainable gardening techniques.
Protecting Your Plants in Rhode Island’s Hardiness Zone
While Rhode Island experiences relatively mild winters, occasional cold snaps can still pose a threat to plants. To protect your plants from frost and freezing temperatures, consider using frost blankets, mulching, or bringing potted plants indoors during extreme weather events. Additionally, proper watering and regular maintenance can help strengthen plants and increase their resilience to harsh conditions.
Conclusion: Navigating Rhode Island’s Hardiness Zone
Understanding Rhode Island’s hardiness zone is essential for successful gardening in the state. By knowing which plants are best suited for the local climate, gardeners can create thriving gardens that not only enhance the beauty of their surroundings but also support the local ecosystem. Taking into account the unique factors influencing Rhode Island’s hardiness zone, such as its geographic location, climate, and proximity to the ocean, will help gardeners make informed decisions when selecting and caring for their plants.