What Are Planting Zones?
Planting zones, also known as hardiness zones, are a system developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) to classify and categorize different regions based on their climatic conditions. These zones provide valuable information to gardeners and farmers about which plants are most likely to thrive in a particular area. By understanding the planting zone of a specific region, individuals can make informed decisions about the types of plants that will grow best in their gardens or farms.
Understanding the Importance of Planting Zones
The importance of planting zones lies in their ability to guide gardeners and farmers in selecting the right plants for their specific area. Each plant has specific temperature requirements for optimal growth and survival. By matching these requirements with the appropriate planting zone, individuals can increase their chances of success in cultivating healthy plants. Planting outside of the recommended zone may result in plants struggling to adapt to the local climate or even failing to survive.
Factors That Determine Planting Zones
Several factors contribute to determining the planting zones of a particular region. The primary factor is the average annual minimum temperature, which helps establish the range of temperatures a plant can tolerate. Other factors include elevation, proximity to large bodies of water, and the effects of microclimates. These factors interact to create a unique climate in each planting zone, defining the types of plants that can thrive in a specific area.
Climate and Planting Zones: The Connection
Climate plays a vital role in determining the planting zones of an area. Temperature, rainfall, humidity, and wind patterns are all key factors that influence the type of plants that can grow successfully. Understanding the climate characteristics of a region is essential in determining the planting zone. This knowledge helps gardeners and farmers make informed decisions about plant selection and growing techniques.
Introducing the Planting Zones of Rhode Island
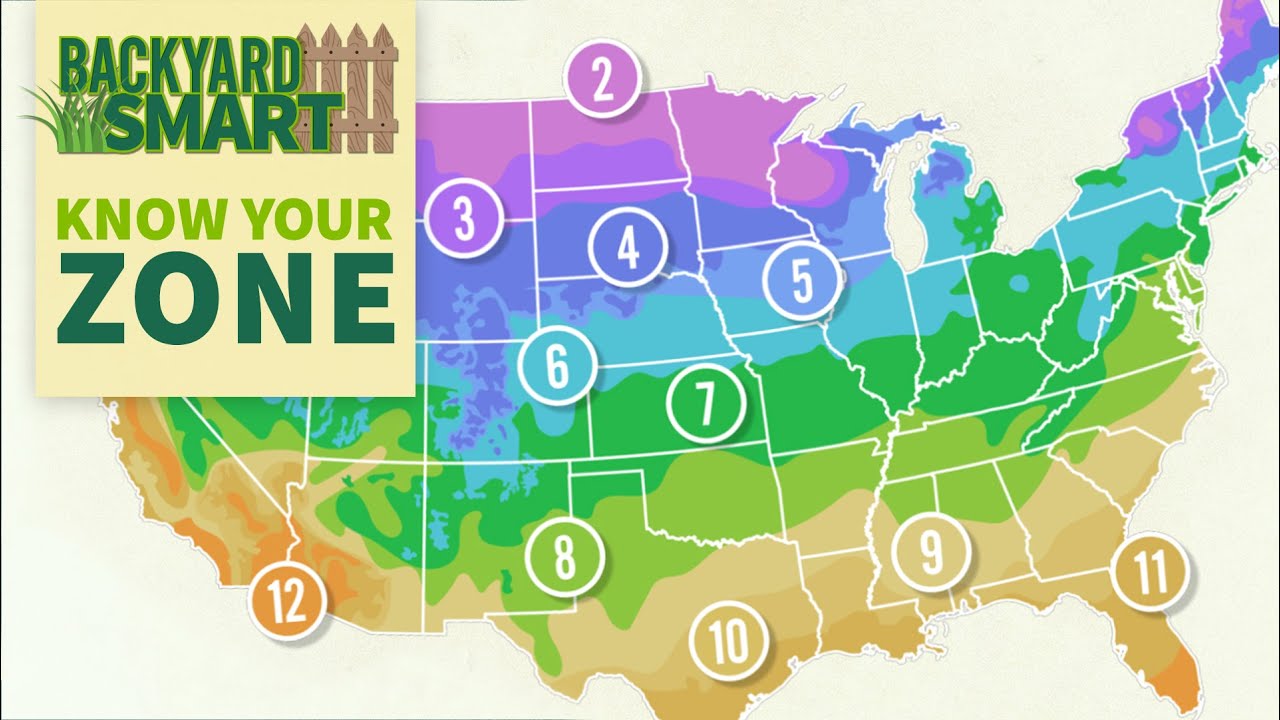
Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States, falls within two planting zones: Zone 6 and Zone 7. These zones are determined by the average annual minimum temperature experienced in the state. Zone 6 covers the majority of Rhode Island, while Zone 7 is found in the southern coastal areas. Each zone represents a specific temperature range, allowing gardeners and farmers to choose plants that are best suited for their location.
Climate Characteristics of Rhode Island
Rhode Island has a humid continental climate, influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean. Summers are typically warm and humid, while winters are cold with the possibility of significant snowfall. The state experiences moderate rainfall throughout the year. These climate characteristics provide a unique environment for gardening, with both advantages and challenges that need to be considered.
Rhode Island’s Unique Planting Environment
Rhode Island’s unique planting environment stems from its small size, diverse topography, and coastal location. The state’s compact size allows for relatively consistent climatic conditions across its territory. Additionally, the varying topography, including coastal plains and hilly regions, creates microclimates that impact local temperature and precipitation patterns. The coastal location of Rhode Island also influences its climate, with milder winters along the coastline due to the warming effect of the ocean.
Identifying Rhode Island’s Plant Hardiness Zone
To identify the specific plant hardiness zone of an area within Rhode Island, it is crucial to consult the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. This map provides detailed information about the average annual minimum temperature across different regions. By locating the specific area within the state, individuals can determine whether it falls within Zone 6 or Zone 7, enabling them to select the appropriate plants for cultivation.
Rhode Island’s USDA Hardiness Zones Explained
Zone 6 in Rhode Island experiences an average annual minimum temperature range of -10°F to 0°F (-23°C to -18°C). On the other hand, Zone 7, found in the southern coastal areas, has an average annual minimum temperature range of 0°F to 10°F (-18°C to -12°C). These temperature ranges provide crucial information about the types of plants that can tolerate the local climate and thrive in Rhode Island.
The Significance of Correct Planting Zones
Planting in the correct zone is crucial for achieving successful gardening results. Choosing plants that are suited to the local climate helps ensure their survival and healthy growth. Plants that are not adapted to a specific zone may struggle to withstand extreme temperatures, leading to stunted growth, disease susceptibility, or even death. By respecting the planting zones, gardeners and farmers can create thriving gardens and productive farms.
Tips for Gardening in Rhode Island Planting Zones
Gardening in Rhode Island’s planting zones requires careful consideration of the local climate and growing conditions. Selecting plants that are known to thrive in Zones 6 and 7 is essential. It is also important to pay attention to the specific microclimates within the state. For example, coastal areas may have slightly milder winters than inland regions. Additionally, providing adequate protection for plants during extreme weather events, such as heavy snowfall or strong winds, can help ensure their survival.
Adapting to Rhode Island’s Planting Zone Challenges
Rhode Island’s planting zones present unique challenges for gardeners and farmers. The state’s relatively short growing season, coupled with the possibility of frost in both spring and fall, requires careful planning and timing of planting. Additionally, the high humidity during the summer months can increase the risk of plant diseases. By selecting disease-resistant varieties, utilizing proper watering techniques, and practicing regular maintenance, individuals can overcome these challenges and achieve successful gardening results in Rhode Island.